 Overview
OverviewA hammertoe is a toe that's curled due to a bend in the middle joint of a toe. Mallet toe is similar, but affects the upper joint of a toe. Otherwise, any differences between Hammer toe and mallet toe are subtle. Both hammertoe and mallet toe are commonly caused by shoes that are too short or heels that are too high. Under these conditions, your toe may be forced against the front of your shoe, resulting in an unnatural bending of your toe and a hammer-like or claw-like appearance. Relieving the pain and pressure of hammertoe and mallet toe may involve changing your footwear and wearing shoe inserts. If you have a more severe case of hammertoe or mallet toe, you may need surgery to experience relief.
Causes
Hammertoes are usually structural in nature. Many times this is the foot structure you were born with and other factors have now made it so that symptoms appear. The muscles in your foot may become unbalanced over time, allowing for a deformity of the small bones in each toe. With longstanding deformity the toe may become rigid. Sometimes one toe is longer than another and this causes a buckling of the digit. A hammertoe may also be caused by other foot deformities such as a bunion. Trauma or other surgery of your foot may predispose you to having the condition if your foot structure is altered.
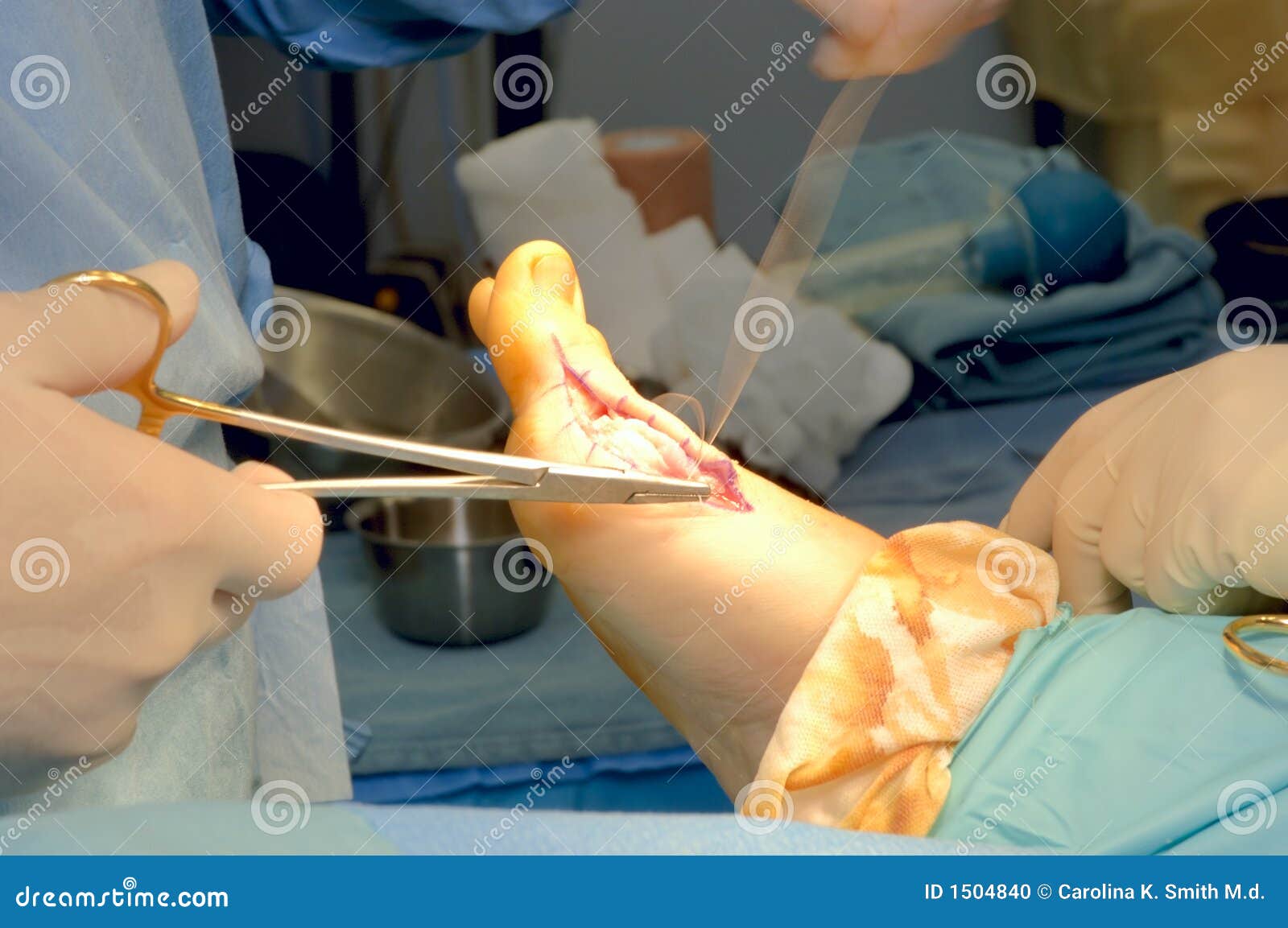 Symptoms
SymptomsFor some people, a hammer toe is nothing more than an unsightly deformity that detracts from the appearance of the foot. However, discomfort may develop if a corn or callus develops on the end or top of the toe. If pressure and friction continue on the end or top of the toe, a painful ulcer may develop. Discomfort or pain can lead to difficulty walking.
Diagnosis
The exam may reveal a toe in which the near bone of the toe (proximal phalanx) is angled upward and the middle bone of the toe points in the opposite direction (plantar flexed). Toes may appear crooked or rotated. The involved joint may be painful when moved, or stiff. There may be areas of thickened skin (corns or calluses) on top of or between the toes, a callus may also be observed at the tip of the affected toe beneath the toenail. An attempt to passively correct the deformity will help elucidate the best treatment option as the examiner determines whether the toe is still flexible or not. It is advisable to assess palpable pulses, since their presence is associated with a good prognosis for healing after surgery. X-rays will demonstrate the contractures of the involved joints, as well as possible arthritic changes and Hammer toe bone enlargements (exostoses, spurs). X-rays of the involved foot are usually performed in a weight-bearing position.
Non Surgical Treatment
To keep your hammertoes more comfortable, start by replacing your tight, narrow, pointy shoes with those that have plenty of room in the toes. Skip the high heels in favor of low-heeled shoes to take the pressure off your toes. You should have at least one-half inch between your longest toe and the tip of your shoe. If you don't want to go out and buy new shoes, see if your local shoe repair shop can stretch your shoes to make the toe area more accommodating to your hammertoe.
Surgical Treatment
If conservative measures fail to provide relief, or if your hammertoe is in advanced stages with rigidity and a significant amount of pain, surgery may be required. Some patients also require surgery if they have open sores or wounds related to their hammertoe. For patients who also suffer from bunions, a combined procedure may be appropriate, addressing both conditions within the same surgery. Recovery time will vary from patient to patient, depending on the extent of the surgical repair and other conditions that may also be present.
 Overview
Overview Symptoms
Symptoms Prevention
Prevention


 Just because a child is active and athletic, they are not immune to foot pain. Such children are susceptible to sprains, strains, and fractures just like an adult. Children also have unique athletic injuries. For instance, active children ages nine to fourteen often can have a severe pain behind the heel. This is due to an inflammation of the growth plate on the back of the heel bone. This syndrome is known as Sever's disease. Like other childhood injuries, this is due to inflammation caused by the Achilles tendon pulling too hard on the back of the heel. The third way to pamper your feet during summer is to increase water consumption, keep them moving, and keep them raised for 20 minutes each day. Summertime can cause swelling in the feet and ankles which can exacerbate conditions such as heel spurs and flat feet. These factors can all contribute to misery after a long day. One suggested excercise that really helps cool the body as well as boost circulation is swimming. If activity, excellent water consumption, and 20 minutes of foot elevation are consistent throughout the summer, feet will be less painful and won't swelling will decrease. Some conditions are easy to see at home, with superficial phlebitis visible to the naked eye. This condition is similar to deep vein thrombosis, and has similar causes, although in most cases is not a serious complaint. It is a blood clot which has formed in the superficial veins on the top of the foot, as opposed to the deep veins where it is a serious health problem. The condition usually presents as inflammation along a vein which is visible through the skin. The clot can cause top of foot pain, and whilst mild in most cases, it is recommended that the problem is still treated by a doctor. Calluses form from repeated friction and pressure, as the shoe (or ground) rubs against a bony prominence (bone spur) on the toe or foot. The skin thickens in response to this pressure. Small amounts of friction or pressure over long periods of time cause a corn or callus. A great deal of friction or pressure over shorter periods of time can cause blisters or open sores. Calluses typically develop under a metatarsal head (the long bone that forms the ball of the foot). Calluses have painful nerves and bursal sacs (fluid-filled balloons that act as shock absorbers) beneath them, causing symptoms ranging from sharp, shooting pain to dull, aching soreness.
Just because a child is active and athletic, they are not immune to foot pain. Such children are susceptible to sprains, strains, and fractures just like an adult. Children also have unique athletic injuries. For instance, active children ages nine to fourteen often can have a severe pain behind the heel. This is due to an inflammation of the growth plate on the back of the heel bone. This syndrome is known as Sever's disease. Like other childhood injuries, this is due to inflammation caused by the Achilles tendon pulling too hard on the back of the heel. The third way to pamper your feet during summer is to increase water consumption, keep them moving, and keep them raised for 20 minutes each day. Summertime can cause swelling in the feet and ankles which can exacerbate conditions such as heel spurs and flat feet. These factors can all contribute to misery after a long day. One suggested excercise that really helps cool the body as well as boost circulation is swimming. If activity, excellent water consumption, and 20 minutes of foot elevation are consistent throughout the summer, feet will be less painful and won't swelling will decrease. Some conditions are easy to see at home, with superficial phlebitis visible to the naked eye. This condition is similar to deep vein thrombosis, and has similar causes, although in most cases is not a serious complaint. It is a blood clot which has formed in the superficial veins on the top of the foot, as opposed to the deep veins where it is a serious health problem. The condition usually presents as inflammation along a vein which is visible through the skin. The clot can cause top of foot pain, and whilst mild in most cases, it is recommended that the problem is still treated by a doctor. Calluses form from repeated friction and pressure, as the shoe (or ground) rubs against a bony prominence (bone spur) on the toe or foot. The skin thickens in response to this pressure. Small amounts of friction or pressure over long periods of time cause a corn or callus. A great deal of friction or pressure over shorter periods of time can cause blisters or open sores. Calluses typically develop under a metatarsal head (the long bone that forms the ball of the foot). Calluses have painful nerves and bursal sacs (fluid-filled balloons that act as shock absorbers) beneath them, causing symptoms ranging from sharp, shooting pain to dull, aching soreness.  If you are on your feet all day, you might suffer from Bunions or you are more prone to develop bunions. Bunions form when the normal balance of forces exerted on the joints and tendons of your feet are disrupted. This can lead to instability in the big toe joint, and can cause a deformity. Bunions develop over years of abnormal motion and pressure to your big toe joints. Heredity can also play a role in the development of Bunions. Other causes of Bunions might be improper fitting shoes that affect the way you walk, foot injuries, deformities present at birth and Neuromuscular disorders. Even though bunions and bunionettes can causes significant side of foot pain , they are often not treated until it is too late. Surgery is called a bunionectomy and involves the removal of excess bone, and the partial destruction of the joint in some cases. Whilst a relatively minor procedure in medical terms, it can be pretty major of the sufferer and can see side of foot pain remain for some time after the procedure. Walking may be difficult, and a splint may be required to keep the toe and the joint in the correct alignment. There is disagreement among medical professionals about the cause of bunions; some see them as primarily caused by the long-term use of shoes, particularly tight-fitting shoes with pointed toes, 1 while others believe that the problem stems from genetic factors that are exacerbated by shoe use. Bunions occur when pressure is applied to the side of the big toe ( hallux ) forcing it inwards towards, and sometimes under or over, the other toes (angulation). As pressure is applied, the tissues surrounding the joint may become swollen and tender. 3.
If you are on your feet all day, you might suffer from Bunions or you are more prone to develop bunions. Bunions form when the normal balance of forces exerted on the joints and tendons of your feet are disrupted. This can lead to instability in the big toe joint, and can cause a deformity. Bunions develop over years of abnormal motion and pressure to your big toe joints. Heredity can also play a role in the development of Bunions. Other causes of Bunions might be improper fitting shoes that affect the way you walk, foot injuries, deformities present at birth and Neuromuscular disorders. Even though bunions and bunionettes can causes significant side of foot pain , they are often not treated until it is too late. Surgery is called a bunionectomy and involves the removal of excess bone, and the partial destruction of the joint in some cases. Whilst a relatively minor procedure in medical terms, it can be pretty major of the sufferer and can see side of foot pain remain for some time after the procedure. Walking may be difficult, and a splint may be required to keep the toe and the joint in the correct alignment. There is disagreement among medical professionals about the cause of bunions; some see them as primarily caused by the long-term use of shoes, particularly tight-fitting shoes with pointed toes, 1 while others believe that the problem stems from genetic factors that are exacerbated by shoe use. Bunions occur when pressure is applied to the side of the big toe ( hallux ) forcing it inwards towards, and sometimes under or over, the other toes (angulation). As pressure is applied, the tissues surrounding the joint may become swollen and tender. 3. Bunions are a very common foot deformity, but it has been seen that people ignore it till the time it takes the shape of a potential hazard for the feet. Bunions are the bumps that occur on the big toe or on its sides. The bump is nothing but it shows the changes that is taking place in the structure of bones of the frontal feet. A person who suffers from a bunion has the big toe pointing towards the second toe instead of its natural straight alignment. Hence, we get to see the bumps in the form of bumps that have fallen out of alignment. read more
Bunions are a very common foot deformity, but it has been seen that people ignore it till the time it takes the shape of a potential hazard for the feet. Bunions are the bumps that occur on the big toe or on its sides. The bump is nothing but it shows the changes that is taking place in the structure of bones of the frontal feet. A person who suffers from a bunion has the big toe pointing towards the second toe instead of its natural straight alignment. Hence, we get to see the bumps in the form of bumps that have fallen out of alignment. read more  Using postoperative orthoses is part of bunion treatment as it helps improve foot functioning while limiting the amount of force on the great toe joint. Your doctor may suggest applying a commercial bunion pad, which is not too stiff or medicated on the bunion or a bunion shield to reduce the pain of the bunion. Inability to Wear Certain Shoes? In this subset of patients, it's the sheer size of the bunion preventing fashionable shoes that motivates treatment - not pain. These patients have learned to live with discomfort but chose fashion over foot health. Clearly, inability to wear shoes is a valid reason for intervention. In this scenario, what do you do for your feet A pedicure once a month is not enough. You need to take care almost on a daily basis. E.g. simply relaxing your feet for ten minutes in a bucket of hot water can do wonders for that aching tired feeling. You may also add a little salt to the bucket for better results. Epsom salt is a good remedy for a strained ligament or a muscle pull. A foot bath is also an excellent way to restore circulation in case you feel numb or cold. For those interested in bunion treatment , you might wonder, “What are bunions”? Bunions ( hallux valgus ) are bony prominences on the outside edge of the big toe where the toe meets the main bones of the foot. Bunions are a combination of three medical conditions that include enlargement of soft tissue; deformities in foot bones, called hallux abducto valgus; and a third condition called metatarsus primus varus. The hallux condition is a rotated big toe that either pushes toward the second toe, sits on top of it, or beneath it. Metatarsus primus is where the bone in the foot connecting to the big toe, rotates outward. 6.If you have bunions and hammertoes, a silicone protective sleeve can help your pain from rubbing in your shoes. Make sure your toe box is wide enough to accommodate the padding. 7.If you have two different sized feet (and most people do), shoe stretchers can be used to stretch the toe box if one foot is only a little bigger than the other. If you have significantly different sized feet, some stores and websites will sell you two different sized shoes. 10.Chunky heels are much more stable than stilettos. Try to wear a wider, more supportive heel or even convert to platforms!
Using postoperative orthoses is part of bunion treatment as it helps improve foot functioning while limiting the amount of force on the great toe joint. Your doctor may suggest applying a commercial bunion pad, which is not too stiff or medicated on the bunion or a bunion shield to reduce the pain of the bunion. Inability to Wear Certain Shoes? In this subset of patients, it's the sheer size of the bunion preventing fashionable shoes that motivates treatment - not pain. These patients have learned to live with discomfort but chose fashion over foot health. Clearly, inability to wear shoes is a valid reason for intervention. In this scenario, what do you do for your feet A pedicure once a month is not enough. You need to take care almost on a daily basis. E.g. simply relaxing your feet for ten minutes in a bucket of hot water can do wonders for that aching tired feeling. You may also add a little salt to the bucket for better results. Epsom salt is a good remedy for a strained ligament or a muscle pull. A foot bath is also an excellent way to restore circulation in case you feel numb or cold. For those interested in bunion treatment , you might wonder, “What are bunions”? Bunions ( hallux valgus ) are bony prominences on the outside edge of the big toe where the toe meets the main bones of the foot. Bunions are a combination of three medical conditions that include enlargement of soft tissue; deformities in foot bones, called hallux abducto valgus; and a third condition called metatarsus primus varus. The hallux condition is a rotated big toe that either pushes toward the second toe, sits on top of it, or beneath it. Metatarsus primus is where the bone in the foot connecting to the big toe, rotates outward. 6.If you have bunions and hammertoes, a silicone protective sleeve can help your pain from rubbing in your shoes. Make sure your toe box is wide enough to accommodate the padding. 7.If you have two different sized feet (and most people do), shoe stretchers can be used to stretch the toe box if one foot is only a little bigger than the other. If you have significantly different sized feet, some stores and websites will sell you two different sized shoes. 10.Chunky heels are much more stable than stilettos. Try to wear a wider, more supportive heel or even convert to platforms!
 You've just finished an enjoyable meal, when your stomach clenches uncomfortably. Muscle cramping is the sensation of a muscle 'locking' in a very contracted position, restricting movement and causing pain. Stomach cramping can be especially difficult to deal with, as nearly all of our movements involve these muscles. Try the following techniques to help alleviate stomach cramping. Although it's recommended to try these steps in order, feel free to reorganize the routine or skip steps if you find it works better for you. Take a hot shower or warm bath to relax the muscles of the affected foot. Another way to do this is to take a warm foot soak. Drop foot, also called foot drop, is the term used for difficulty in lifting the front part of the foot. It is easily recognized by the dragging of the front of the foot as a person walks. Sometimes foot drop is temporary, other times it is a permanent condition. Knee swelling may also be referred to as water on the knee or as knee effusion. Knee swelling may be a symptom of a disease, medical condition or an injury. Swelling may be accompanied by pain and stiffness. If these conservative treatments fail to provide pain and pressure relief it may be necessary to have surgery to correct the Hammer Toe. Nearly all of Dr. Blitz’ patients are walking immediately after hammer toe surgery in a stiff soled surgical shoe. Sometimes, patients may have the bunion repaired at the same surgical setting, and that may dictate whether or not walking would be allowed. Because of Dr. Blitz’ advanced bunionplasty techniques he is able to weightbear a very larger majority of the bunions (regardless of severity) – so having hammer toe surgery doesn’t change that variable in his patients. Laser Hammer Toe Surgery Exercises usually include physical and occupational therapy modalities. Range-of-motion exercises, exercise in whirlpool or warm swimming pool, remaining active all help decrease the immobility produced by the disease. The primary objective of your rehabilitation program is to regain pain free range of motion in your ankle joint and lower leg. As your ruptured Achilles tendon heals, you can begin gentle movements such as bending and straightening your ankles. As your progress and become more comfortable with bending and straightening your ankles, you can begin to rotate them from side to side, and then rotate your ankles clockwise and counter clockwise. Once your regain pain-free range of motion in your ankles, you can proceed to active rehabilitative exercises. You Might Also Like Stretching Exercises
You've just finished an enjoyable meal, when your stomach clenches uncomfortably. Muscle cramping is the sensation of a muscle 'locking' in a very contracted position, restricting movement and causing pain. Stomach cramping can be especially difficult to deal with, as nearly all of our movements involve these muscles. Try the following techniques to help alleviate stomach cramping. Although it's recommended to try these steps in order, feel free to reorganize the routine or skip steps if you find it works better for you. Take a hot shower or warm bath to relax the muscles of the affected foot. Another way to do this is to take a warm foot soak. Drop foot, also called foot drop, is the term used for difficulty in lifting the front part of the foot. It is easily recognized by the dragging of the front of the foot as a person walks. Sometimes foot drop is temporary, other times it is a permanent condition. Knee swelling may also be referred to as water on the knee or as knee effusion. Knee swelling may be a symptom of a disease, medical condition or an injury. Swelling may be accompanied by pain and stiffness. If these conservative treatments fail to provide pain and pressure relief it may be necessary to have surgery to correct the Hammer Toe. Nearly all of Dr. Blitz’ patients are walking immediately after hammer toe surgery in a stiff soled surgical shoe. Sometimes, patients may have the bunion repaired at the same surgical setting, and that may dictate whether or not walking would be allowed. Because of Dr. Blitz’ advanced bunionplasty techniques he is able to weightbear a very larger majority of the bunions (regardless of severity) – so having hammer toe surgery doesn’t change that variable in his patients. Laser Hammer Toe Surgery Exercises usually include physical and occupational therapy modalities. Range-of-motion exercises, exercise in whirlpool or warm swimming pool, remaining active all help decrease the immobility produced by the disease. The primary objective of your rehabilitation program is to regain pain free range of motion in your ankle joint and lower leg. As your ruptured Achilles tendon heals, you can begin gentle movements such as bending and straightening your ankles. As your progress and become more comfortable with bending and straightening your ankles, you can begin to rotate them from side to side, and then rotate your ankles clockwise and counter clockwise. Once your regain pain-free range of motion in your ankles, you can proceed to active rehabilitative exercises. You Might Also Like Stretching Exercises The fungus which affects toenails is a living organism which thrives in damp and dark environments good examples are the region between your nails and toes. This fungal infection is actually very common and affects millions of people across the world every year. The numbers however are probably conservative given a large proportion of sufferers do not seek medical advice. Include one session of yoga in your weekly workout regimen. Yoga strengthens your muscles, including those in your calves, but also works to relieve muscle tension throughout your body. Yoga helps to lengthen and relax contracted muscles in the lower legs.
The fungus which affects toenails is a living organism which thrives in damp and dark environments good examples are the region between your nails and toes. This fungal infection is actually very common and affects millions of people across the world every year. The numbers however are probably conservative given a large proportion of sufferers do not seek medical advice. Include one session of yoga in your weekly workout regimen. Yoga strengthens your muscles, including those in your calves, but also works to relieve muscle tension throughout your body. Yoga helps to lengthen and relax contracted muscles in the lower legs.  During your workout, some exercises require more support than others. Running places severe pressure on the feet. Running shoes are made for different arch types, so running shoes are built with arch supports. If you are on your feet for long periods, you are putting stress and strain on your feet so exercises such as walking or using the elliptical will also be straining if you don't have enough support. Those who have lower arches or who overpronate excessively may need to wear supportive shoes or orthotics all the time, not just while exercising, according to the Sports Injury Clinic. Strengthening the Arch I myself, have suffered from fallen arches. I would unexpectedly get 'pulled muscles' in my legs and have sore toes after playing sports during the past year until about three months ago my left leg became so bad, it wouldn't heal after nearly a month so I had to go to a Physiotherapist. There, she told me that I had fallen arches and would have to pay at least €100 for off-the-shelf orthotics that I'd have to wear for the rest of my life. I was lucky that my feet weren't severe enough to need that yet. When you have Plantar Fasciitis avoid any activity that can further aggravate the problem. This includes walking for long distances, walking up or down stairs, running, sports etc. If you want to keep fit swimming is the safest activity, until your heel pain has been treated properly. Or you can ride a bike or a stationary exercise bike. Basically, try to be as little on your feet as possible, allowing the plantar fascia to heal itself. Plantar fasciitis – This condition is characterized by heel pain, especially with the first few steps you take. The plantar fascia stretches as the arch falls, putting stress on the heel. Dr. Steven P. Shelov points out in his book, “Your Baby’s First Year,” that only one or two out of 10 children actually end up having flat feet into adulthood. There are various types of foot issues that can cause irregular foot conditions, including tightness of the heel cord, rigid arches or flat feet. Foot Issues and Concerns You might ponder why shoes are cushioned, and some need inserts. What purpose does putting padding on the bottom, the sides, or extra pieces that you can add in otherwise serve? Will it help your feet overall with more padding or less and are all shoes created equal in this matter? The Plantar Fascia acts as a 'bowstring' connecting the ball of the foot to the heel. It forms the longitudinal arch of the foot and helps to lift the heel off the ground to prepare the foot for the 'take-off' (propulsive) phase of the gait cycle. During walking, at the moment the heel begins to lift off the ground, the Plantar Fascia endures tension that is around twice our body weight. The Plantar Fascia also act as a natural shock-absorber during walking and running. However, long term, effective treatment of Plantar Fasciitis consists of a simple program of daily stretching exercises, combined with wearing an orthotic to support the arches.
During your workout, some exercises require more support than others. Running places severe pressure on the feet. Running shoes are made for different arch types, so running shoes are built with arch supports. If you are on your feet for long periods, you are putting stress and strain on your feet so exercises such as walking or using the elliptical will also be straining if you don't have enough support. Those who have lower arches or who overpronate excessively may need to wear supportive shoes or orthotics all the time, not just while exercising, according to the Sports Injury Clinic. Strengthening the Arch I myself, have suffered from fallen arches. I would unexpectedly get 'pulled muscles' in my legs and have sore toes after playing sports during the past year until about three months ago my left leg became so bad, it wouldn't heal after nearly a month so I had to go to a Physiotherapist. There, she told me that I had fallen arches and would have to pay at least €100 for off-the-shelf orthotics that I'd have to wear for the rest of my life. I was lucky that my feet weren't severe enough to need that yet. When you have Plantar Fasciitis avoid any activity that can further aggravate the problem. This includes walking for long distances, walking up or down stairs, running, sports etc. If you want to keep fit swimming is the safest activity, until your heel pain has been treated properly. Or you can ride a bike or a stationary exercise bike. Basically, try to be as little on your feet as possible, allowing the plantar fascia to heal itself. Plantar fasciitis – This condition is characterized by heel pain, especially with the first few steps you take. The plantar fascia stretches as the arch falls, putting stress on the heel. Dr. Steven P. Shelov points out in his book, “Your Baby’s First Year,” that only one or two out of 10 children actually end up having flat feet into adulthood. There are various types of foot issues that can cause irregular foot conditions, including tightness of the heel cord, rigid arches or flat feet. Foot Issues and Concerns You might ponder why shoes are cushioned, and some need inserts. What purpose does putting padding on the bottom, the sides, or extra pieces that you can add in otherwise serve? Will it help your feet overall with more padding or less and are all shoes created equal in this matter? The Plantar Fascia acts as a 'bowstring' connecting the ball of the foot to the heel. It forms the longitudinal arch of the foot and helps to lift the heel off the ground to prepare the foot for the 'take-off' (propulsive) phase of the gait cycle. During walking, at the moment the heel begins to lift off the ground, the Plantar Fascia endures tension that is around twice our body weight. The Plantar Fascia also act as a natural shock-absorber during walking and running. However, long term, effective treatment of Plantar Fasciitis consists of a simple program of daily stretching exercises, combined with wearing an orthotic to support the arches.  RSS Feed
RSS Feed